- Medical
Psoriasis
Understanding Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that speeds up the skin cell cycle and leads to thick, red, scaly plaques that may itch, sting, or feel tight. Plaques can appear anywhere, most often on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back, and may also affect the nails. The condition typically cycles through flares and periods of remission, which can affect comfort, confidence, and daily life.
Psoriasis can be associated with other health concerns, including psoriatic arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic conditions. Not everyone with psoriasis will experience these issues, but they are important to consider during evaluation and long term management.
Causes and Triggers
Psoriasis results from an immune system misfire that signals the skin to produce cells more quickly than normal. Genetics and environment both play a role. Common triggers include skin injury, infections, certain medications, cold or dry weather, stress, smoking, and heavy alcohol use. Identifying and reducing personal triggers helps limit flares and supports better control.
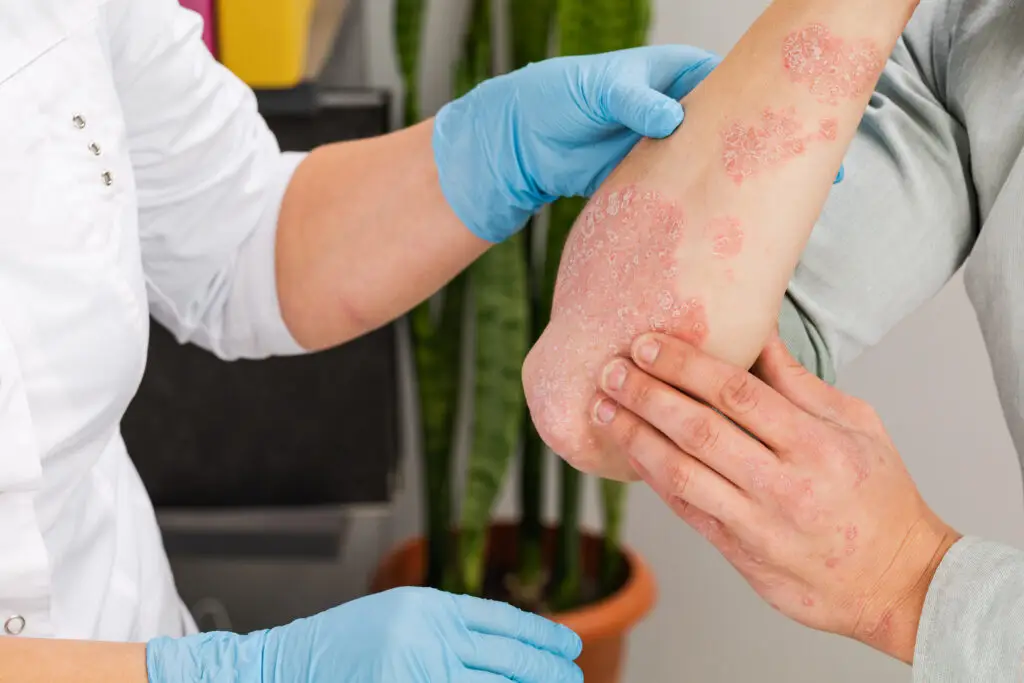
Common Types
Plaque psoriasis is the most common form. It presents as raised, red plaques with a silvery scale on areas such as the knees, elbows, lower back, and scalp. Plaques can crack, bleed, burn, or itch and may cause nail pitting or separation.
Treatment Options
Treatment is individualized based on severity, body areas involved, type of psoriasis, and medical history. Plans often combine therapies to improve control while protecting the skin barrier.
Topical therapies
Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and itching
Vitamin D analogs to slow skin cell growth
Topical retinoids to normalize turnover
Calcineurin inhibitors for sensitive areas such as eyelids or skin folds
Keratolytics like salicylic acid to lift scale and enhance penetration of other medicines
Phototherapy
Narrowband or broadband UVB to slow abnormal growth
PUVA, which combines a light sensitizer with UVA under supervision
Systemic and advanced therapies
Traditional systemic medicines such as methotrexate or cyclosporine for moderate to severe disease
Oral agents such as apremilast to reduce inflammatory signaling
Biologic medicines that target specific immune pathways and have been highly effective for many patients
Lifestyle and supportive care
Regular use of emollients and ointments to reduce dryness and scale
Stress management and sleep support to limit flare frequency
Thoughtful diet and weight management as part of overall health
Trigger awareness, gentle skin care, and sun protection
Our Approach
At Heritage Dermatology, we begin with a careful evaluation of your skin, nails, joints, health history, and treatment goals. Together we build a stepwise plan that balances results, safety, convenience, and cost. Education on home care and trigger management is part of every visit, and we adjust your plan as your skin changes over time.
You do not have to manage psoriasis alone. Schedule a visit with Heritage Dermatology to create a personalized plan that calms flares, protects long term health, and helps you feel comfortable in your skin.